Does Forage Particle Size Affect Heifer Distiller Grains Utilisation?
Particle size is important for digestion in cattle, but there was little difference between growth performance of heifers fed either chopped or pelleted diets in a recent study.The growth performance and total tract nutrient digestion of heifers fed diets high in distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) was investigated using different forage particle sizes.
Particle size affects rumen fermentation and rumination, as large forage particles help stimulate rumination which aids in buffering with saliva, according to researchers at South Dakota State University.
Buffering may be important when considering feeding DDGS because it is considered an acidic feedstuff with a pH near 4.0.
Additionally, forage particles size can affect the passage rate out of the rumen and consequently affect the utilisation of DDGS, because it has a high rumen undegradable protein (RUP) content compared to traditional feeds like soybean meal.
Therefore, it is possible that heifers fed pelleted alfalfa hay may have differences in rumen fermentation, which is evaluated by volatile fatty acids (VFA) production and pH.
Total tract nutrient digestibility, and subsequently different heifer growth may also differ because of the faster feed passage rate out of the rumen and less rumen buffering.
Heifers put on the study had a 2-week training period in which they were trained to use the feeding system used for monitoring individual intakes and fed a ramp-up diet to allow time for adjustment to the experimental rations.
Treatment diets were either 15 per cent chopped (CHOP) or 15 per cent pelleted (PELL) alfalfa hay on a dry matter (DM) basis.
All the diets also contained 30 per cent DDGS, 53.75 per cent corn silage, and 1.25 per cent mineral mix and were limit-fed for dry matter intakes (DMI) at 2.3 per cent of body weight (BW).
Heifers were limit-fed to target an average daily gain (ADG) of 1.8 lb/d. Another benefit of limit-feeding is there were minimal refusals and it eliminated any issues with ration sorting as heifers consumed all of their feed.
Growth performance was evaluated by body frame measurements, body weights, and body condition scores (BCS) which were taken on two consecutive days every two weeks during the study.
During week 8, an external marker (titanium dioxide) was fed for 10 days prior to fecal grab samples were taken to measure total tract nutrient digestion. Heifers fed the CHOP diet had more dry matter intake than the heifers on the PELL diet (9.7 and 9.23 lb/d for CHOP and PELL, respectively).
Different diets had limited effects on heifer growth
Body weights (368.3 and 360.8 lb) and average daily gain (1.83 and 2.11 lb/d) were similar between treatments, but gain to feed ration however was found to be less in CHOP versus PELL.
Frame measurements including hip heights, withers heights, and body lengths were similar between treatments. All other measurements including paunch girths, heart girths, and hip widths were slightly greater for CHOP compared to PELL. However, BCS was less for CHOP versus PELL.
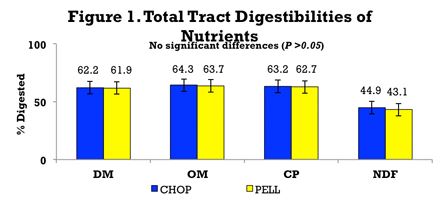
We did not find significant treatments by week interaction or differences in average daily changes for growth measurements. When fecal samples were analysed it was found that total tract digestion of dry matter (DM), organic matter (OM), neutral detergent fiber (NDF), and crude protein (CP) were similar among treatments (Figure 1).
This study demonstrated that heifers fed diets high in DDGS, with 15 per cent of the forages being chopped or pelleted alfalfa hay, had similar growth performance and total tract nutrient digestion.
However, some body measurements such as hip widths, paunch and heart girths slightly increased, while gain to feed and BCS decreased by feeding chopped versus pelleted hay.
Overall, forage processing to achieve different forage particle size does not have a major impact on utilisation of DDGS by growing heifers.